Abstract
Introduction
Central nervous system (CNS) involvement is an extremely rare manifestation of extramedullary multiple myeloma (MM), diagnosed in less than 1% of MM patients (pts). It is considered an ultimate high-risk feature, associated with unfavorable cytogenetics, and, even with intense treatment applied, survival is short, reaching less than 12 months in most cases.
Case
An 81y old male pt. with κ light chain MM on serum and urine, osteolytic lesions and bone marrow involvement in 2015, was referred to our institution. He presented with a CNS MM relapse in June 2017 after prior successful 1st line Bortezomib-based treatment. Cranial MRI confirmed multiple supra- und infratentoral lesions infiltrating the brain. His cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) demonstrated a high load of clonal plasma cells (PMCs) and κ free light chains (FLC), however, the disease was largely absent within the bone marrow of the patient.
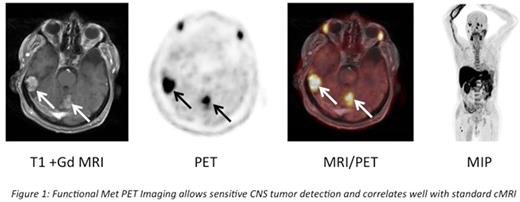
The use of positron emission tomography (PET) with 18F-2`-deoxy-2`-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) in MM has been strengthened by the recent publication of the updated imaging guidelines by the IMWG (Cavo et al., Lancet Oncol, 2017). Standard FDG based CNS imaging resolution, however, is impacted by the increased baseline glucose metabolism background of the brain. Therefore, we used radiolabeled 11C-methionine (MET) - that we recently identified as a sensitive imaging tracer in MM and in fact, high metabolic activity could be detected supra- and infratentorial as well as in the right femur and the clivus (Lapa et al., Theranostics, 2016).
The pt. received 3 courses of an intrathecal triple therapy (Cytarabin, MTX, Dexamethasone) leading to a significant reduction of PMC-burden in the CSF. In addition, age adjusted systemic Thiotepa/Cytarabin-based therapy was applied, but had to be discontinued after one course of treatment as grade 4 neutropenia occurred with life-threatening septicemia.
In parallel, we analyzed CD138+ cells obtained from BM and the CFS using customized next generation targeted sequencing (Ion torrent platform). The M3P (v 3.0) gene selection includes most commonly mutated MM genes, actionable drug targets and genes being associated with drug resistance. Average sequencing depth increased 700X and spatial MM heterogeneity was detected, as the CFS cells harbored a clonal BRAFV600E mutation, which was absent in the germline control and the bone marrow based CD138+ cells.
We have initiated targeted therapy using the combination of Dabrafenib/Trametinib, known to be effective in BRAFV600E mutant melanoma brain metastases (Davies MA et al., Lancet Oncol, 2017); responses will be followed by combined cMRI and MET-PET imaging and results will be displayed at the meeting.
Conclusion:
This is an example of spatial genomic heterogeneity in MM and the first report of a patient with an isolated brain based BRAFV600E mutated MM tumor. This patient with otherwise very limited perspective leverages from innovative diagnostics including MET PET and targeted genome sequencing, demonstrating their clinical utility as they provide the basis for precision medicine concepts to be applied in this MM patient.
Stewart: Amgen: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal